At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
How Do Doctors Remove a Pancreatic Stent?
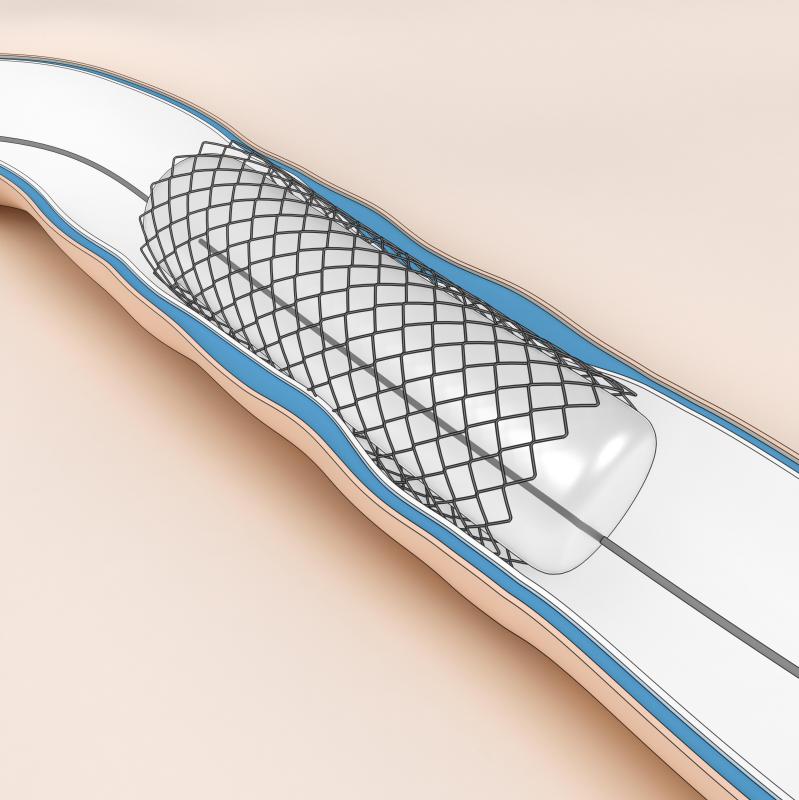
A pancreatic stent is a thin tube surgically implanted into a pancreatic duct to allow drainage. Stents are typically removed using endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or duodenoscope-assisted cholangiopancreatoscopy (DACP). Before the procedure, patients will be sedated, and an X-ray might be taken of the area to view the position of the stent. An endoscope and sometimes a duodenoscope will then be used to view the pancreatic duct while the surgeon removes the stent using forceps or a snare. After the procedure, patients might be required to attend several post-operative check ups to observe the results of their stent removal.
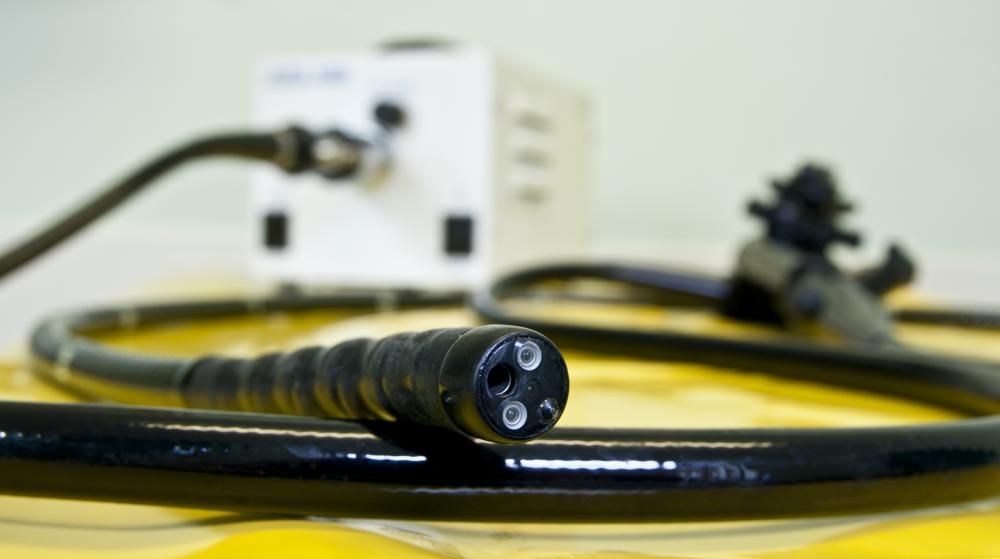
Pancreatic stents are commonly removed with the help of ERCP. This is a procedure that involves the use of radiography and a specialized endoscope. An endoscope is a tool that projects images of internal organs, tissues and other structures onto a viewing screen when inserted into the body. Endoscopes are hollow, which also makes it possible for doctors to insert and use specialized tools. In some cases, a duodenoscope is also used to view the gastrointestinal tract.

Before removing a pancreatic stent, patients are sedated and given a local anesthetic to numb the throat. General anesthesia, which will put the patient into a deep sleep, can also be used during this procedure. This will depend on the patient’s anxiety level, the preference of the surgeon, and the complexity of the procedure. To prepare for the procedure, the surgeon might also take X-rays of the pancreatic stent to determine whether the object has migrated or shifted.

Once the patient has been sedated, the individual will be shifted onto his or her side, and the endoscope will be inserted into the mouth. The endoscope will be guided down the esophagus, through the stomach and to the pancreatic stent. If necessary, the endoscope can also be inserted through a small incision in the abdomen. Upon reaching the area, the endoscope will project the image of the duct, stent and surrounding tissues onto a viewing screen. If the surgeon needs a better view of the pancreatic stent, a duodenoscope can also be used to view the area.

The surgeon will then grasp the stent using a snare or endoscopic forceps. If the stent has shifted, a small needle-knife incision will be made in the pancreatic duct to make the stent more accessible. The stent will be pulled from the duct and removed through the instrument channel. Whenever possible, stents are removed without causing injury to the ducts or surrounding tissues.

After stent removal, the endoscope will be removed from the patient. If an incision has been made, the wound will be cleaned and closed. The patient will be supervised while he or she regains full consciousness. To ensure the pancreatic stenting was successful, patients will usually be required to make several post-operative visits to their physician. During these appointments, the physician will determine whether the pancreatic duct is draining properly or if additional treatment is required.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discuss this Article
Post your comments