At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What are Atypical Glandular Cells?
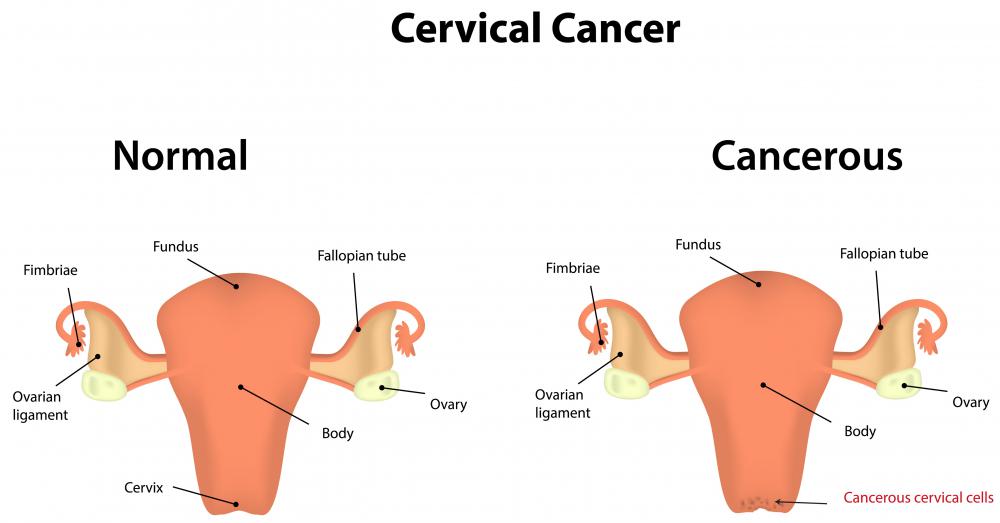
Atypical glandular cells are cells found in a mucousal region, primarily the cervix, which are behaving abnormally. They may be growing at a faster pace than normal or they may have a strange appearance that is not typical of normally functioning cells. This is generally a more severe indication of cancer than squamous cell abnormalities and these cells should be looked into carefully to ensure that they are not malignant.
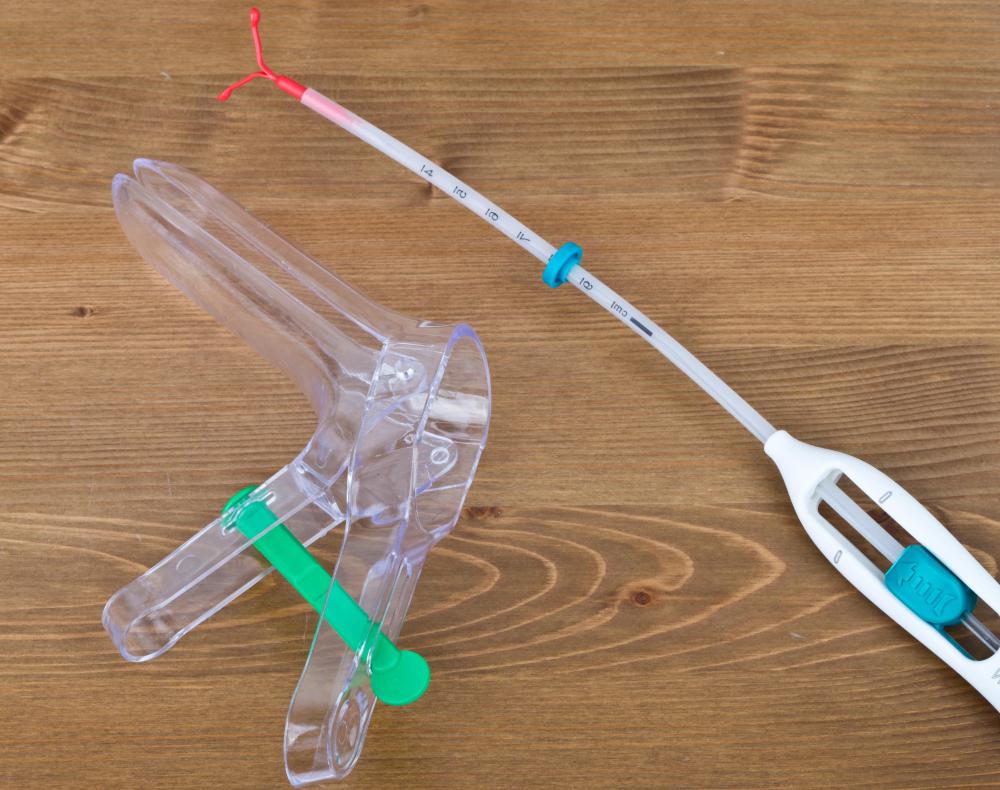
Many times, atypical glandular cells are found in the cervix. They are often caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) and can indicate cervical cancer or pre-cancer. Most often they are found through a pap smear, which is an exam in which a doctor takes samples of cervical tissue for testing. If atypical cells are found, a biopsy may be performed to determine if they are cancerous.

Not all atypical glandular cells indicate cancer. Sometimes they are considered pre-cancerous, which simply means that they are abnormal and may turn into cancer at a later time. At other times they may be caused by the virus and cause complications aside from cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer is generally slow growing, but the type caused by atypical glandular cells is often more aggressive than cancers that form on the outer cells. Women are strongly encouraged to get a pap smear once every year starting at around age 18, or when they become sexually active. Every three years is recommended after at least three consecutive normal exams.

There are vaccinations to help prevent HPV infection, since this virus causes the majority of atypical glandular cells which lead to cervical cancer. Practicing safe sex is also recommended since HPV is sexually transmitted. This can help women avoid cervical cancer in many cases.
Treatment for atypical glandular cells will depend on how abnormal they are and whether or not they are found to be cancerous. Non-cancerous cells may be treated with the “wait and see” approach with more frequent testing to ensure that they do not become cancerous over time. Cancer may be treated by freezing off the cancerous tissue, surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation treatment, depending on how severe it is and whether it has spread.

Cervical cancer is highly treatable when found early. The cure rate is extremely high since this type of malignancy generally spreads very slowly. When not treated in its early stages, it may spread to the uterus. For this reason, testing is very important.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:
















Discussion Comments
My sister had atypical glandular cells on her pap smear recently and she was terrfied that she might have cancer. The doctor assured her that it was unlikely at her age, but still she was a nervous wreck until they got the results in.
Apparently, quite often they get atypical results and have to check. The pap smear is only the first stage of the process and an abnormal pap smear doesn't really tell them very much, except that there might be a problem.
In the end, it turned out my sister was fine, but they want her to go in and get checked every year, rather than every three years, which she is more than happy to do.
Pap smears are so important. If you haven't had one in a while, you should book yourself an appointment.
@Iluviaporos - It's not so much that they always think their kids will go out and have sex after having the vaccination, as that they just don't see the point in having it when they don't expect their child to have sex at all until marriage. And, of course, the man will be completely faithful, so no danger there either.
Unfortunately, the world doesn't work like that. If nothing else, even the most perfectly chaste woman might be sexually assulted.
HPV is so very prevalent most adults have it, so all it would take is one encounter with a sexually active person, and you would have the disease that can cause these atypical glandular cells.
It's better to be safe than sorry, and the vaccination does no harm, so why not have it?
There has been a lot of controversy over the vaccination for HPV infection.
I can see why it might be a sore spot for some people, but really, what it comes down to is trusting your kids. Just because they get one more vaccination, doesn't mean they'll feel they have permission to go and have sex with whoever they want.
I mean, in reality HPV isn't something that would stop teenagers from having sex in the first place. So why not just get them vaccinated as a matter of course? It would seriously cut down on the number of cervical cancer if everyone was vaccinated for it, like they are for the measles.
Post your comments