At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Are Neurochemicals?
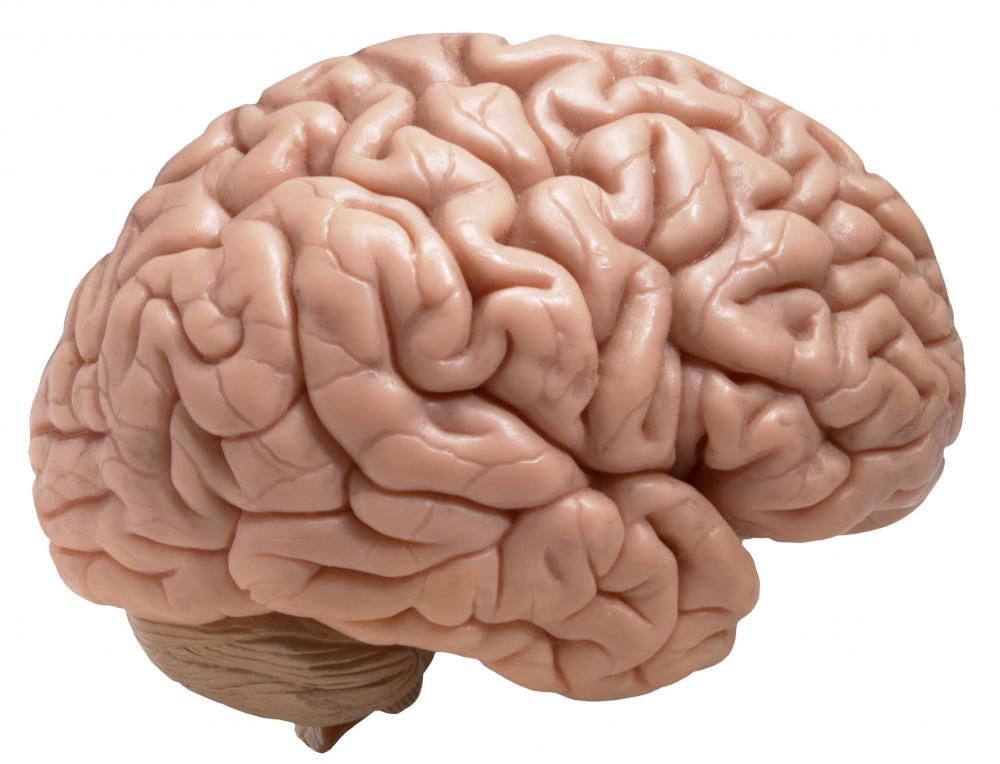
Neurochemicals are chemicals involved in the functioning of an organism's nervous system. They have purposes such as regulating thoughts and emotions, transmitting signals from neurons, and promoting the growth and repair of the nervous system's cells. A person's neurochemistry can have profound effects on his or her health, abilities, and behavior. Psychoactive drugs affect the user by altering his neurochemistry, and many health problems and disorders are the result of the sufferer's inability to produce or absorb neurochemicals in proper amounts.
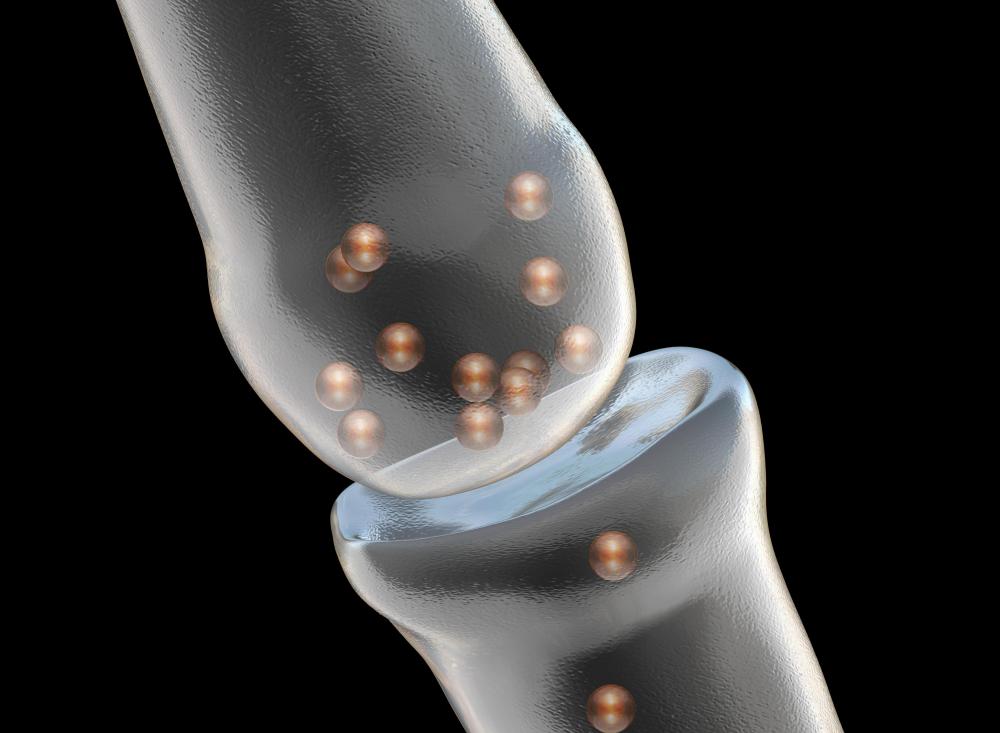
One major type of neurochemicals is the neurotransmitter, which crosses the synapses between neurons to transmit signals. The most common neurotransmitter in humans is glutamate, which is important in learning and memory. Excessive glutamate levels can poison nerve cells and cause stroke, mental retardation, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, also known as Lou Gehrig's disease. There are also indications that excessive levels of glutamate can cause seizures.

Dopamine is a neurotransmitter affecting a variety of mental functions, including memory, motivation, and voluntary motor control. It is important to the brain's reward system, which causes pleasurable sensations by releasing dopamine in response to stimuli such as food, sex, and other sources of enjoyment. Insufficient dopamine levels are implicated in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and cause the motor control problems, such as tremor and slowed movements, suffered by people with Parkinson's disease.

Serotonin is a neurotransmitter important to the digestive system and to an organism's perception of resources such as food. Some primitive animals release serotonin when food is detected, while in humans serotonin is released after food has been consumed, reducing appetite. Serotonin is also related to perceptions of social power, dominance, and submission. Serotonin is released when food is detected in the gastrointestinal tract, causing contractions that push the food through the tract. Serotonin levels rise when toxins are detected, either increasing contractions to push the irritant through the gastrointestinal tract and out of the body more rapidly or, in extreme cases, activating chemoreceptors that induce vomiting in order to expel whatever unwholesome substance has been ingested as quickly as possible.

Endorphins are neurotransmitters produced during times of intense sensation, such as pain, sexual climax, and physical exertion. It is an endogenous opioid that blocks sensations of pain and can cause feelings of well-being or euphoria. Some people who engage in deliberate self-harm, such as cutting their own skin, do so because the endorphins released in response to the injury can cause temporary relief from stress or depression.

The hormone oxytocin is a neurotransmitter important in social bonding, sexual arousal, and maternal behavior. Increased levels of oxytocin produce feelings of calm, contentment, and trust. The release of oxytocin and the chemically similar hormone vasopressin during sexual activity is believed to reinforce monogamous pair bonding. Oxytocin is also released during breastfeeding and promotes maternal bonding.

Not all neurochemicals are neurotransmitters. Neurotrophins promote the health and survival of existing neurons and stimulate neurogenesis, the creation of new neurons. Examples of neurotrophins include brain-derived neutrotrophic factor and nerve growth factor, both of which are important to the health of the nervous system. Animals unable to properly produce neurotrophins have problems with neural development, resulting in neurological defects and premature death.

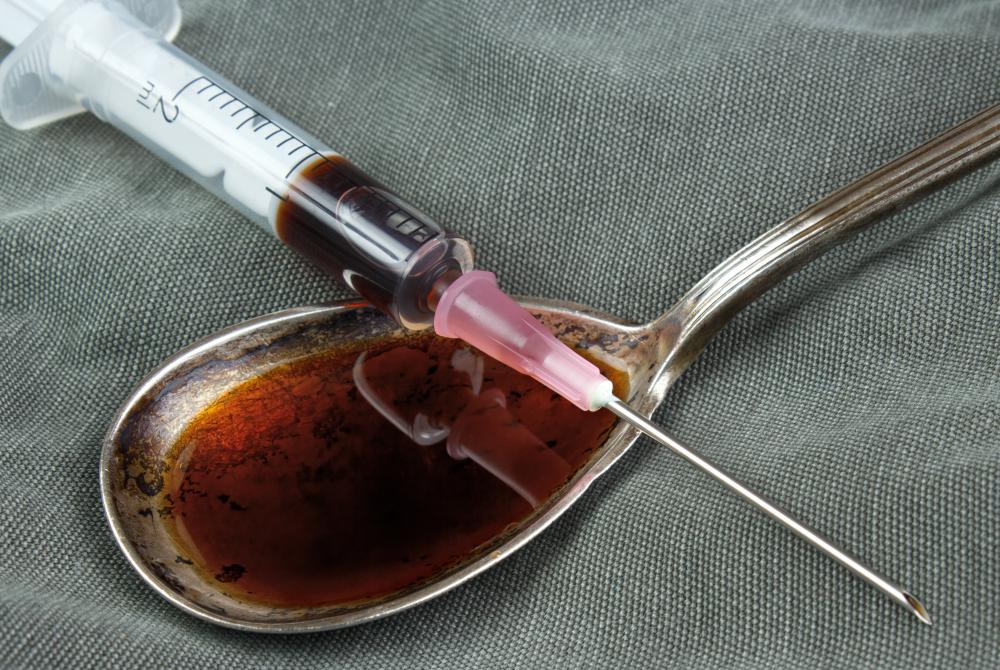
Neurochemicals are essential to the effects of recreational drug use. Endogenous opioids such as morphine and heroin cause pain relief or feelings of euphoria through a mechanism similar to that of endogenous opioids such as endorphins. Most recreational drugs produce at least part of their pleasurable effect by stimulating the release of dopamine, and this interaction with the brain's reward system is an important factor in drug addiction. The overstimulated brain eventually starts reducing the production of dopamine and dopamine receptors in response to the excess, dulling the addict's response to pleasurable stimuli in general and requiring the addict to increase his consumption of the drug to produce the same pleasurable sensations as before.

Neurochemical abnormalities are implicated in a number of mental disorders. Scientists have hypothesized that obsessive-compulsive disorder may be caused by a deficiency in the reception of serotonin, resulting in increased anxiety. Some scientists have also speculated that excessive production of or sensitivity to dopamine causes psychosis and schizophrenia. Schizophrenics show increased activity in some of their dopaminergic pathways, which transmit dopamine around the brain. Antipsychotic drugs work mostly by blocking dopamine reception, and temporary psychosis can be induced by drugs that cause extreme increases in dopamine levels, such as cocaine and amphetamines.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are neurochemicals?

Neurochemicals are substances that are secreted by nerve cells in the nervous system and brain and act as messengers for the transmission of messages between neurons. These chemicals control mental and bodily functions, including memory, emotions, and behavior.
What are the different types of neurochemicals?
Neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, and neurohormones are the three primary categories of neurochemicals. The most typical sort of substance in charge of transmitting impulses between neurons is a neurotransmitter. Neuromodulators are involved in altering the intensity of impulses between neurons, whereas neurohormones are produced from neurons and affect other cells in the body. These three different classes of neurochemicals are necessary for the healthy operation of the nervous system and the brain.
What effect do neurochemicals have on the brain?

Neurochemicals are essential for regulating mental processes and brain function. Neurotransmitters enable communication between various areas of the brain by relaying messages between neurons. Neuromodulators alter the intensity of these impulses, which may impact the duration a neuron is active and the quantity of information passed on. Information can be transmitted between cells and organs thanks to neurohormones, which are released from neurons and act on other cells in the body.
How are neurochemicals regulated?
A multitude of distinct processes control neurochemicals. The action potentials of neurons govern the release of neurotransmitters, while other neurons and body cells control the release of neuromodulators and neurohormones. Reuptake, a process in which the neurotransmitter is taken up into the neuron from whence it was released, is another mechanism that controls the quantity of neurochemicals present in the brain. This procedure makes sure that the brain's neurochemical equilibrium is maintained.
What part do neurochemicals play in maintaining mental health?
For the brain to operate properly and to control physical and mental functions, neurochemicals are required. Bipolar illness, anxiety, and sadness are just a few of the mental health issues that may be brought on by neurochemical imbalances. For instance, it is believed that depression is brought on by a serotonin neurotransmitter imbalance. In contrast, bipolar disorder is thought to be brought on by an imbalance of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Also, it is well-recognized that neurohormones like cortisol control stress and may contribute to the development of mental diseases.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discussion Comments
I'd like to know if cerebrospinal fluid can be considered a neurochemical since it is an organic substrate and is present in the nervous system.
Post your comments