At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Are the Common Causes of Blood Clots in the Placenta?
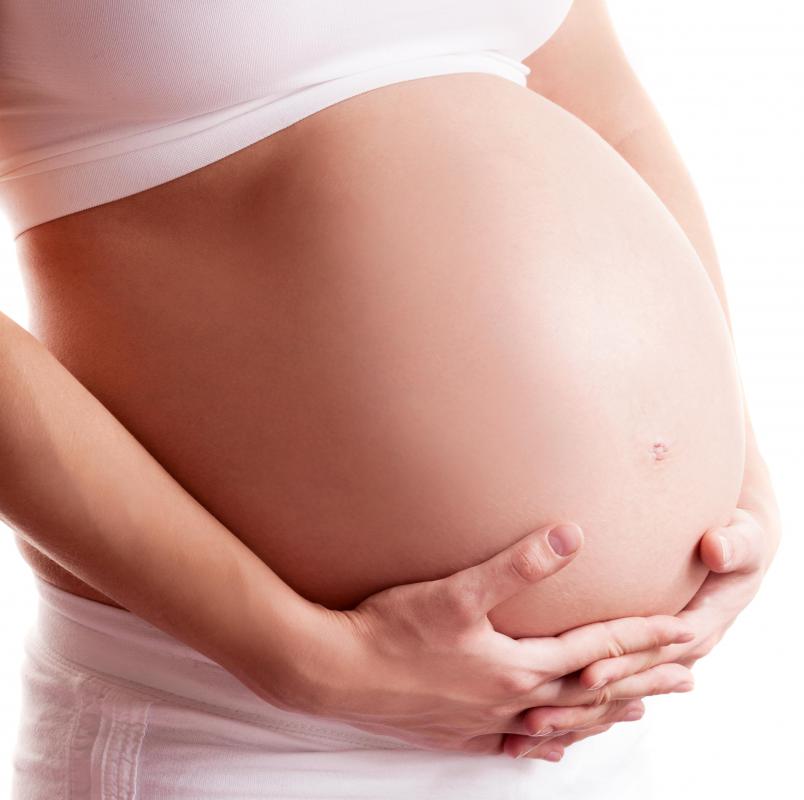
Common causes of blood clots in the placenta include thrombophilia, an inherited or acquired disorder of the blood, or improper formation of the placenta during pregnancy. Both conditions might cause birth defects, miscarriage, or premature birth. Thrombophilia can be treated with blood thinning medications during pregnancy, but other causes of clots might not be discovered until after birth or miscarriage.
Several forms of thrombophilia exist, with two types linked to genetics. The acquired form represents an autoimmune disease that might cause complication in about five percent of pregnant women. Thrombophilia occurs when blood produces too much of a specific protein that causes it to clot. The blood might also create too little of another protein that prevents clots from forming. About half of all cases of blood clots in the placenta are linked to thrombophilia.

Women with a history of this disease face greater risks of blood clots in the placenta during pregnancy. The disorder might also lead to placental abruption, a condition where the placenta tears away from the uterine wall. Placental abruption poses serious risks to the fetus and mother. It might provoke miscarriage after 10 weeks' gestation and produce a stillborn child in the second or third trimester of pregnancy.

Some women with thrombophilia are treated with blood thinning medication while pregnant and six weeks after delivery. They typically receive injections of heparin one or more times a day while carrying a child. This drug does not cross the placenta into the fetal bloodstream. Doctors typically prescribe low-dose aspirin as part of the treatment for blood clots in the placenta.

Once a child is born, women commonly continue with oral medication to thin the blood. Warfarin is commonly used at this point, with or without continued use of heparin. Not all pregnant women diagnosed with thrombophilia require treatment. Physicians look for previous complications during pregnancy, the severity of the disorder, and family history to determine if medication is necessary. Side effects of these drugs might lead to bone loss.

The placenta develops inside the uterus during pregnancy to nurture the fetus as it grows. One part of the placenta attaches to the uterine wall as a conduit to the mother’s blood supply. An umbilical cord links the baby to the placenta as a source of oxygen and nutrients from the mother’s blood.
Fetal waste material is also transported via the umbilical cord to the mother’s blood for disposal through her kidneys. Nutrients supplied by the placenta also protect an unborn child from infection. Hormones in the tissue also signal when labor should start. Once a baby is born, the placenta has served its purpose and is expelled. If blood clots form in placental vessels, they might restrict the flow of oxygen to the fetus, which could cause birth defects.

Blood clots in the placenta might also develop if the placenta forms incorrectly. It might grow too thinly or too thickly, or the umbilical cord improperly attaches. Blood clots from these conditions might also cause infection or areas of tissue death. This might lead to developmental delay of the fetus, premature birth, miscarriage, or excessive bleeding during childbirth.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discuss this Article
Post your comments