At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Are the Common Causes of Choking on Saliva?
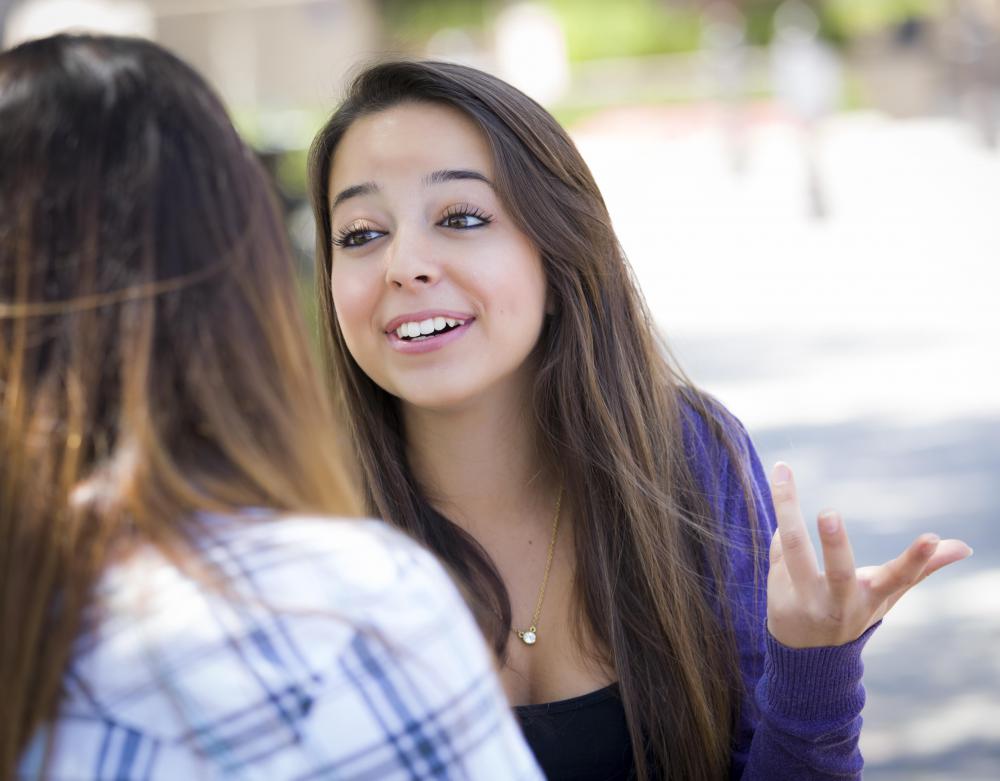
The most common causes of choking on saliva are excessive saliva production, certain throat and swallowing problems, and neurological disorders that can cause numbness or temporary paralysis of the muscles that normally regulate swallowing. It’s not that unusual for people to choke on their own saliva from time to time, and in most cases this isn’t a major concern. Infrequent choking episodes might be caused by something as simple as talking too quickly or moving the head too fast while trying to swallow. Gagging and choking is usually something people should be concerned about when it seems to happen often, though, or when bouts appear to be getting more intense. A medical check-up can often help people in this category get to the root of the problem and find a solution before things get worse.
Excessive Saliva Production

The main goal of saliva is to help with food digestion and preliminary breakdown, and it’s produced by salivary glands. Humans typically have three main glands of this sort; one sits below the tongue, one is within the jaw, and the largest is just above the throat. Ideally, each produces saliva in response to certain environmental triggers. Sometimes signals can be misread or misinterpreted, though, which can lead to overproduction.

When one or more glands produces too much fluid it can create more than a person can readily cycle out with a regular swallow. Saliva often pools in the back of the mouth as a result, and can cause gagging or choking. These effects are often most pronounced when lying down, but can strike at any time. Overproduction issues can sometimes be tamed by changes in diet, but medication may also be required to bring things back into balance.
Throat and Swallowing Problems

A number of medical problems with the throat might also be to blame, since these often impact how well or how frequently a person is able to swallow. Lesions in the throat, tumors, and severe arthritis are some of the most common. The severity will depend on how serious the condition is. Reflux-related lesions can often heal themselves after awhile once the condition is treated, but cancer or tumors of the throat are much harder to treat and tend to get worse the more time passes. Those with large tumors may experience feelings of tightness in the throat, and breathing can eventually become more difficult.

People might also find themselves choking or gagging as a result of some sort of injury to the throat or esophagus. In these cases choking is usually an early indication that something is wrong, but is just one of many symptoms. Pain, bleeding, heartburn, and cough are frequently also present.
Neurological Disorders
Some more serious diseases can also lead to swallowing problems and saliva choking episodes. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is one example. ALS is a fatal neurological disorder that affects a person’s ability to use certain muscle systems. As the nerves die, the ability to perform basic bodily functions or movements becomes impossible. The inability to swallow is usually a later symptom of the illness, and choking on saliva becomes a very real possibility during this stage. The use of suction devices to clear the throat of any excess is often needed on an ongoing basis.
Incapacitation

Choking is also a more serious risk among heavy drinkers. Alcohol can slow the body’s response time, and drinking to the point of incapacitation often causes people to do such things as wet themselves and swallow their own vomit. A person who loses consciousness in this state in a position where saliva can pool in their throats — splayed over a couch with the head tipped back, for instance — may choke on spittle, particularly if he or she is prone to producing more than necessary in the first place.
When to Get Help
Nearly everyone chokes or coughs on their own saliva at some point in their life. This is usually not indicative of any medical condition, and is often just the result of forgetting to swallow often enough or talking too quickly. When it occurs only occasionally in this way, there is no cause for concern, and a doctor's advice is usually not required.
Most experts recommend that people get evaluated when they’ve been noticing symptoms for a long time, or in cases where the choking or gagging is near-constant or is otherwise interfering with daily life. Getting a diagnosis can lead to treatment, and with luck the problem will go away. It’s also the best way to rule out more serious conditions. Identifying things like ALS and throat cancer early on can improve prognosis and might even be able to delay or eliminate more serious later symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens when saliva gets stuck in the airway?
Saliva that becomes stuck in the airway may obstruct airflow and deprive the body of oxygen. Choking on saliva is a disorder that may be brought on by weaker gag reflexes, anatomical anomalies, or foreign objects in the airways. It is a medical emergency that has to be attended to right away.
What are the signs of choking on saliva?
Chest pain, coughing, gagging, and vomiting are all signs of choking on saliva. In extreme circumstances, the individual may lose consciousness or be unable to summon assistance.
Who is most susceptible to choking on saliva?
The most vulnerable groups to choking on saliva are infants, young children, and the elderly. Although older individuals may have trouble swallowing due to muscular weakness and reduced saliva production, infants and young children have lower gag reflexes.
What causes choking on saliva?
Choking on saliva can be caused by a weakened gag reflex, anatomical abnormalities, or foreign objects in the airway. A weakened gag reflex can result from medication, illness, or fatigue. Anatomical abnormalities can obstruct the airway, while foreign objects can become lodged in it.
How can choking on saliva be prevented?
Choking on saliva can be prevented by avoiding behaviors that increase the risk, such as drinking alcohol or taking medication that affects the gag reflex. It is also important to avoid talking while eating or taking large bites of food. Infants and young children should be supervised during meals and playtime to prevent the accidental inhalation of foreign objects.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discussion Comments
How often is too often? Should I be concerned about choking too much on my saliva? I mean how many times a week is too much that I should see a doctor about?
My son had this problem when he was a toddler. He would get a lot of saliva when he was teething and sometimes he would choke on it. It was very scary for me and I would pat him on his back, but he always recovered very quickly. He totally grew out of this though and it wasn't a problem at all after he was three.
@ddljohn-- There are many possible reasons. You should probably see a doctor about it since you said that it's happening very frequently.
When you wake up at night, do you have to spit to get rid of saliva? If so, it sounds like a case of excessive saliva production, but you need to get a test to confirm that. It could also be post-nasal drip from your sinuses or acid reflux.
Do you have sinus problems or GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)? Congested or infected sinuses can cause post-nasal drip where fluid drips to the back of your throat. You might be choking on this at night and thinking that it's saliva. Sometimes GERD also causes this. Acid reflux can trigger saliva production or the acid can irritate the throat causing coughing and choking like symptoms.
Unfortunately, no one can diagnose you over the net, so see a doctor soon.
I wake up several times every night choking on saliva. It started several weeks ago and I don't know what to do about it. I keep a glass of water by my bed and I prop up pillows but it still happens. What might be the cause?
Post your comments