At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Are the Different Types of Fibromas?
Fibromas, also known as fibroid tumors, fibroids, and fibromatous or fibroblastic tumores, can be found in all organs. Common benign fibroid tumors are classified as hard, soft, or uterine. Other types of fibroid tumors exist but do not fall into one of these groups, are often found in other areas or organs. In some cases, the cells in a fibroid tumor can be cancerous. The tumor is then classified as a fibrosarcoma.
Connective, or fibrous, tissue is the structure that forms the benign fibromas. Mesenchyme tissue, a type of connective tissue found in a fibroma, contains cells that are loose instead of compressed. This tissue can also form cartilage, standard connective tissue, and help develop the lymphatic and circulatory systems. When this form of tissue remains fibrous, a fibroma is more likely to develop.

Hard fibroid tumors, called fibroma durum, are comprised of more fibers with fewer cells. The extra fibers make the tumors much harder than other types. They are most commonly found in the jaw or mouth. In many cases, tumors form between the teeth and jaw bone and may also be accompanied by calcified tissue that closely resembles the consistency of bone.
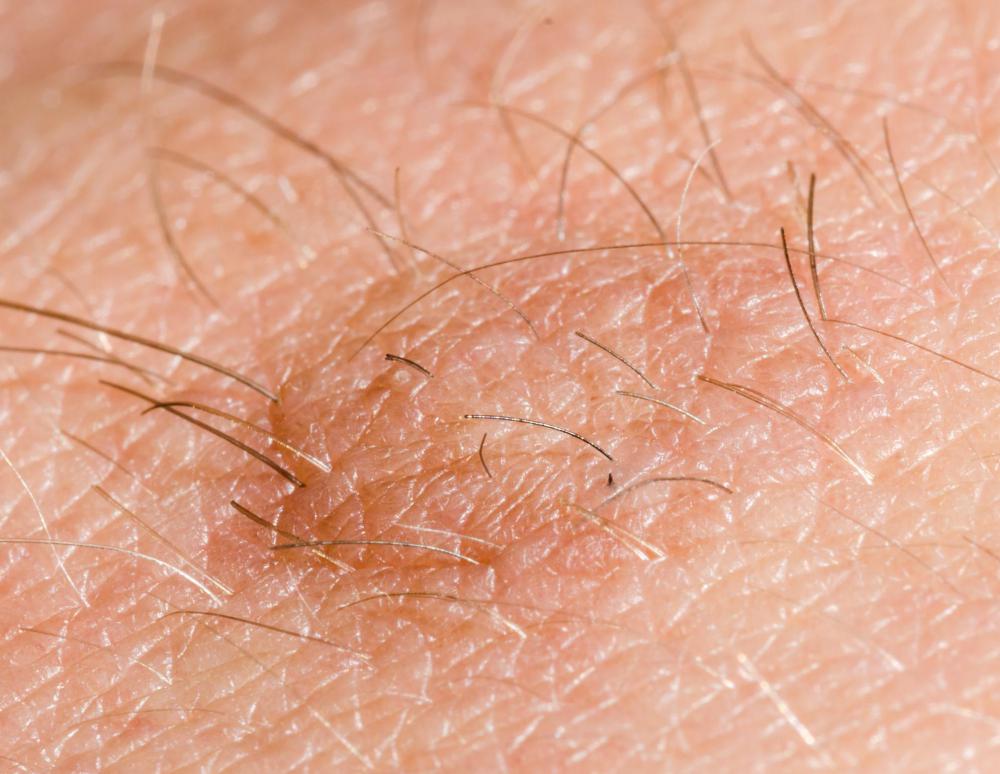
Soft fibromas, called fibroma molle, contain more cells that are loosely connected and not as many fibers. These tumors have a shaft. They most commonly occur on the neck, skin, armpit, and groin areas where the skin rubs together.

Uterine fibroids grow in the uterine wall, partially in the uterine cavity and outside the uterine wall. This type of tumor is the most common for women. Most fibroid uterine tumors go undetected unless they lead to problems and complications. Problematic tumors can cause abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, and infertility.
Other types of fibroid tumors are classified by their location, similar to the way uterine fibroid tumors are classified. These tumors can be found on or in any organ. Examples include fibroid tumors of the nasal passage, lungs, and ovaries.

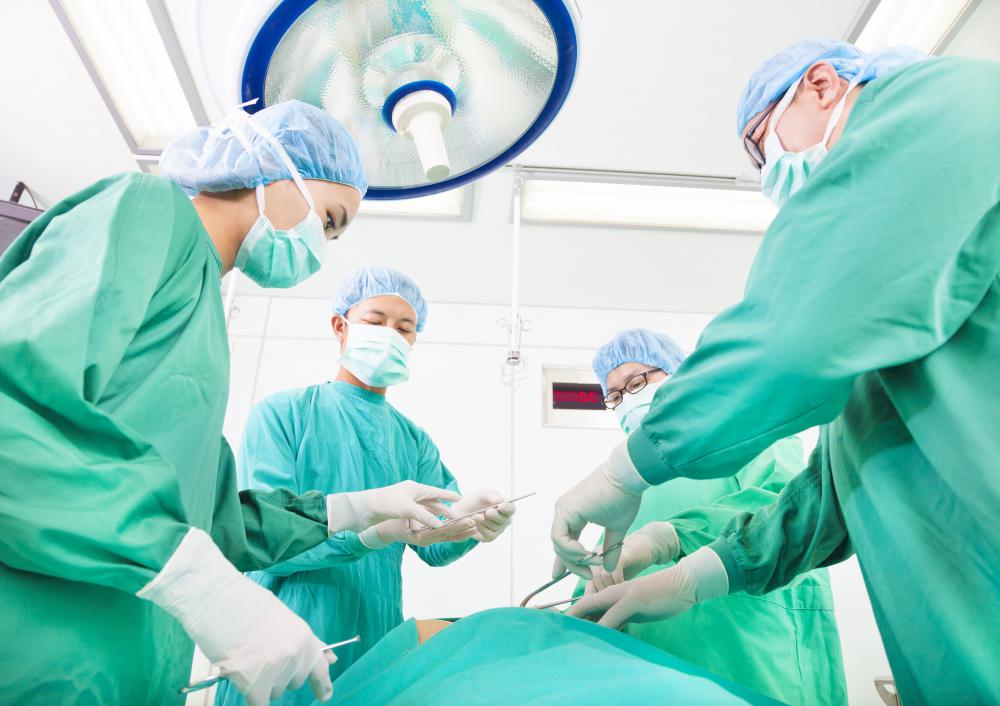
Many fibromas do not cause symptoms, and they generally go undetected until problems do occur. Doctors may decide to biopsy a fibroma that is discovered to determine if it is benign. For those that are problematic, surgery is often recommended to remove the tumor. Cancerous fibroid tumors are almost always removed, except in cases where removing the fibroma would be life-threatening.

The surgery performed to remove fibromas is done on a same day outpatient basis. For more complicated removals, a prolonged hospital stay may be necessary. Regardless of how long the hospital stay will be, recovery from the surgery is going to take time.
Initially, the patient will have limitations on activity levels. The doctors will provide post-operative care instructions, and follow up appointments are required. Healing progress is checked and the patient is monitored for signs of infection, including fever and redness around the incision. In instances of cancerous fibroids, further treatment and monitoring is necessary to ensure the fibroids do not regrow.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discussion Comments
@serenesurface-- Doctors don't know exactly what causes various types of fibromas. But I think that underlying conditions may be a factor. For example, those with genetic disorders or chronic diseases may be at bigger risk.
In class, we learned about a case of ossifying fibroma. I had never seen a growth so large! It was located inside the mouth and had grown to a huge size. It was removed completely with surgery.
It seems that many fibromas don't turn cancerous. But they cause complications because they can grow and damage nearby tissues and bones. So I think that they need to be diagnosed and removed to avoid these problems.
My little brother had a hard fibroma removed from his mouth. He didn't even feel that it was there for the longest time. I asked why it occurred and the doctor said that there isn't a particular reason. It's so strange.
My sister has a fibroadenoma in her breast. I'm not an expert on this topic but I know that it's a type of fibroid cyst. Thankfully, it's benign, so it's harmless. But she does have to have a mammogram and physical once every six months to make sure that the cyst is not growing.
Initially, a doctor had suggested removing the cyst. But my sister got opinions from several other doctors. The majority opinion was to leave it alone since it's not growing and it's benign. Moreover, it turned out that my sister has a different breast tissue texture and they are not even one hundred percent sure that it's a fibroma. There is a small chance that it might just be a normal part of her natural breast tissue. So it is not being removed for this reason. We hope that it will always remain small and benign.
Post your comments