At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is Severe Dysplasia?
The term dysplasia refers to any type of abnormal physical development. It is most often used to refer to cellular abnormalities, which are often pre-cancerous, but can also be used to describe a deformation of the hip joint. Although severe dysplasia can indicate any type of high grade abnormalty, it is frequently used as a short-hand for severe cervical dysplasia, which can be a precursor of cervical cancer. Also known as carcinoma-in-situ, this is a condition in which the skin of the cervix is growing at an abnormally fast pace.
As a result of this abnormal growth, there is an increased amount of immature skin cells present on the surface of the skin or lining of the cervix. While this rapid growth of cells takes place on the surface of the cervix, the chances of developing into an invasive cancer are very high. This means early detection and treatment is extremely important.

Severe dysplasia is one of three different types of cervical dysplasia currently identified in medical circles. Mild dysplasia, also known as CIN 1, is a condition where there are relatively few immature skin cells present, although more than considered normal. Moderate dysplasia, or CIN 2, has a higher and more widely disbursed amount of immature cells. The third category of dysplasia, or CIN 3, is the most serious category, since the number of immature cells is extremely high and is causing a noticeable change in the thickness of the surface layer of the cervix.

One of the conditions that can trigger severe dysplasia is known as the human papillomavirus, or HPV. This virus can infect different types of epidermal layers as well as the mucous membranes in the human body. HPV can pave the way for cancers in several parts of the body, including cervical cancer.
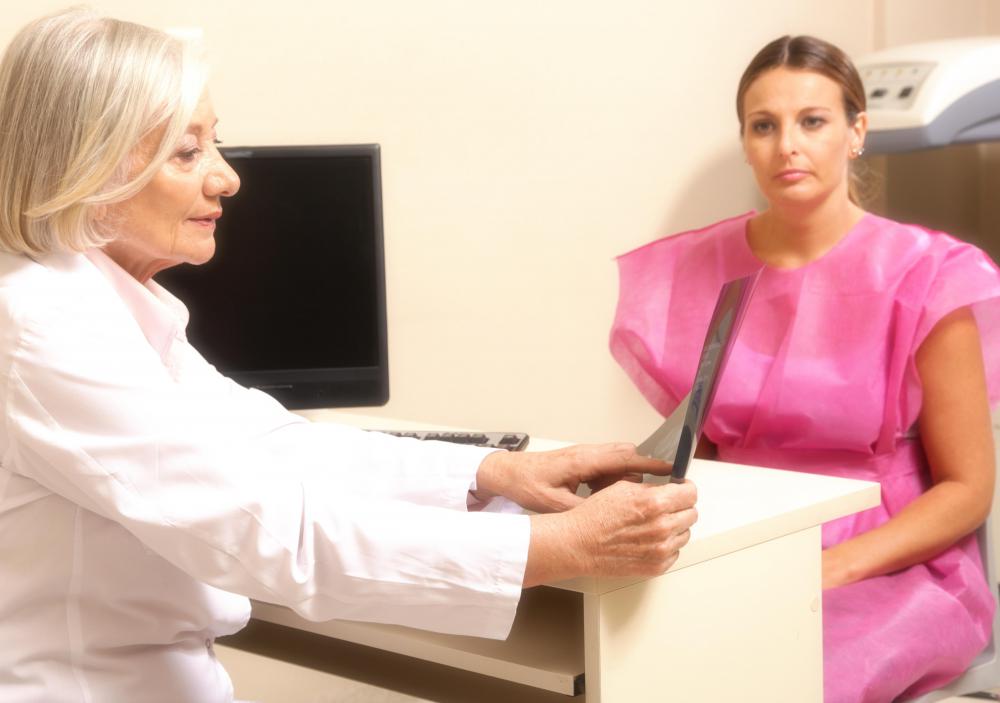
Detecting this condition involves the use of a Pap smear. Samples obtained during the smear can be analyzed to determine the presence as well as the current status of the dysplasia. This allows the physician to take action before there is a chance for the proliferation of immature cells to begin penetrating the surface of the cervix and pave the way for the development of cervical cancer.

In some cases, there may also be evidence of what is known as a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, or HGSIL. A lesion of this type is also identified during the course of a Pap smear, and is an indication of the presence of moderate to severe dysplasia. While not an indicator that cancer is already present, these lesions do indicate that conditions are rapidly approaching the point where cancer could develop.

When HGSIL is found, physicians usually order what is known as a colposcopy. This procedure involves the removal of samples of the tissue. In some cases, the dysplastic tissue is completely removed. In both scenarios, the removed tissue is submitted for biopsy, making it possible to confirm whether or not cancer is forming, and also to determine the current status of the dysplasia itself.

Additional treatments for severe dysplasia may involve the use of cryotherapy, some type of cauterizing, or even laser surgery to remove the excess skin cells. Physicians rarely employ any of these treatments if the female is currently pregnant, however, fearing that they could have an adverse effect on the pregnancy. Instead, the condition is monitored, and removal of the excess epidermal layer on the cervix is accomplished at some point after the delivery.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:
















Discussion Comments
This is one of those illnesses that can be treated really easily but can become deadly if it is ignored. They say that about 30% of severe dysplasia of the cervix develops into cancer. That is a huge number! That means at least one out of five severe dysplasia patients will have cancer!
But all we have to do is visit our doctor often for checkups and rush to the hospital if there are lesions or random bleeding. Prevention is the best cure!
@simrin-- That's a great question. As far as I know, it isn't caused by menstruation or child birth. Like the article said, it is mostly caused by sexually transmitted viruses that cause lesions in the genital area. It somehow changes into dysplasia and possibly into cancer eventually.
I actually read something really interesting in a women's magazine. Researchers have found a connection between smoking and cervical cancer. So the chances of having dysplasia is possibly higher if you smoke.
I read that the main role of the cervix is to allow menstruation and child birth. Does severe dysplasia have anything to do with menstrual problems and giving or not giving birth?
My friend had HPV with severe dysplasia of the cervix. After her abnormal pap smear she went back to the doctor to have a colposcopy and biopsy done. It was pretty unsettling and the tests did come back to show that she would need further treatment. That led to what's called a LEEP, or Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure, wherein the doctor used a thin wire loop electrode to cut away the affected cervical tissue in the immediate area of the loop wire. Some people have it done in the hospital and are sedated, while others have it done in their physician's office. It sounds scarier than it is, and she recovered pretty quickly. Now she's had normal pap smear results.
Post your comments