At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Striated Muscle?
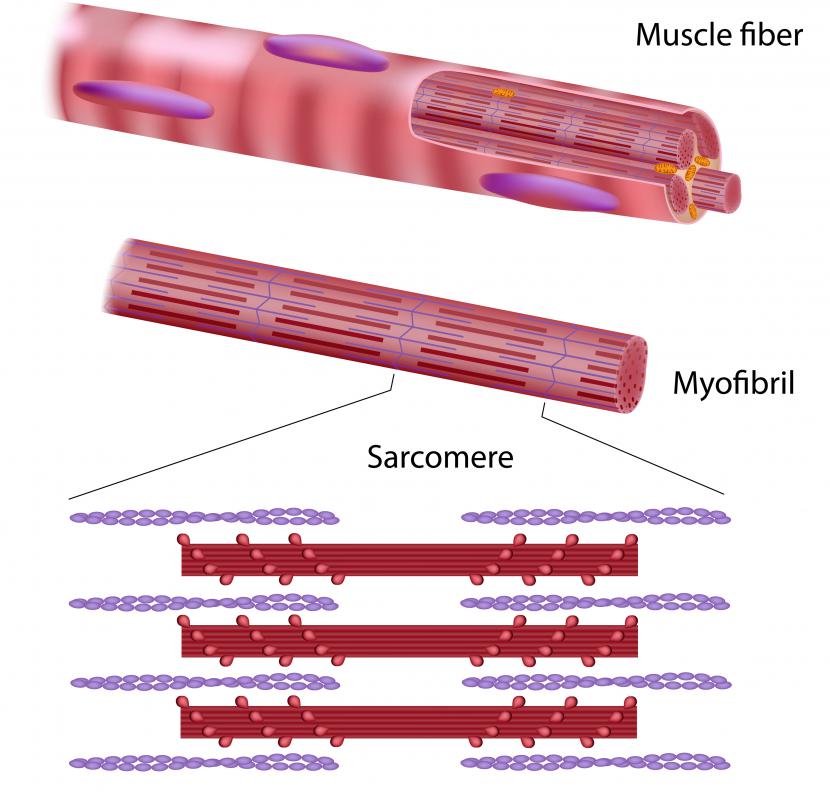
A striated muscle is a muscle composed of thousands of units known as sarcomeres. Each sarcomere is composed of distinct bands of different material which give the muscle a striped or striated appearance when it is viewed at a high level of magnification. These muscles move when various bands within the sarcomeres contract or relax, causing the muscle as a whole to shorten or extend. The interactions between bands in the same muscle are designed to keep the muscle moving smoothly and powerfully through a flexing motion or extension.
There are two types of striated muscle: skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. The skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles which allow for the movement of bones and joints, while cardiac muscles are involuntary, and found only in the heart. The cardiac muscle also has a slightly different appearance from skeletal muscle, although both share the striated trait characteristic of muscle tissue which contains sarcomeres.

Some people use the term “striated muscle” to refer specifically to skeletal muscle, separating cardiac muscle into another category to avoid confusion. These muscles all have a point of attachment known as the origin where the muscle connects to a bone, and a point where the muscle meets a tendon, known as the insertion. When the muscle contracts, it pulls the tendon, causing a flex, and when the muscle relaxes, an extension occurs. Striated muscles usually work in pairs, with one relaxing and one contracting, to keep movements smooth and even.

Striated muscle is the most common type of muscle tissue in the body. It can be found in both slow and fast twitch forms. Fast twitch muscles can produce a burst of high energy for rapid and powerful movement, but they tire quickly. Slow twitch muscles produce less energy, but are designed for endurance and sustained work. People can further condition their muscles through exercises which are designed to improve muscle tone, stamina, and function.

While the striated skeletal muscle is primarily controlled by the body, it can also be involved in involuntary movement. Many of the skeletal muscles will react in a reflex when triggered to do so, and they also help to maintain posture by maintaining a specific tension level and position which keeps the skeleton together and in alignment. As many people have learned, posture can be influenced through exercise and concentration, illustrating the difference between striated muscle which is toned and exercised, and those which are not.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discussion Comments
@robbie21 - The opposite of striated muscle is smooth muscle. Contraction of smooth muscles is involuntary; you don't control it, which is probably why you don't think of smooth muscle when you think of "a muscle."
Smooth muscle is found in lots of places in your body, including your blood vessels and your digestive tract. These internal systems use contraction to move things along, digest your food, etc., but you don't have any control over it and usually don't feel it. One exception: The uterus is a giant smooth muscle (that's why OBs talk about "contractions") and that one, people feel when it contracts!
OK, so I get the idea that striated muscle is basically what I think of when I think of a muscle. Like the biceps or hamstring. So what's non-striated muscle? Is all muscle striated? Or maybe just all human muscle?
Post your comments