At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is Ubiquinone?
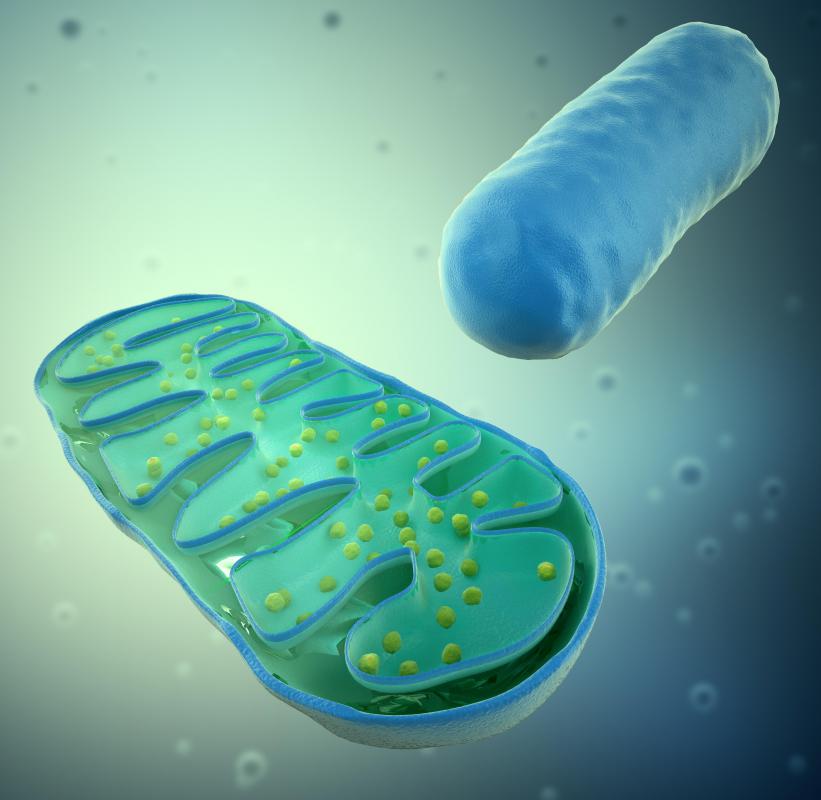
Ubiquinone, or coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), is generally found in most eukaryotic cells as a naturally-occurring substance, as well as in many foods. It is most abundant in the cell mitochondria of organs with high energy requirements, such as the heart, kidneys, and liver. CoQ10 plays an important role in aerobic cellular respiration, and its main function is to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), thus providing the cell with energy.
In addition to the cell mitochondria, ubiquinone can also be found in other organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum, vesicles, lysosomes, and peroxisomes. As for food sources, beef, pork, and chicken hearts are generally the richest sources of CoQ10. Other good sources may include meats, fish, oil, nuts, and vegetables.

Certain factors may affect the levels of ubiquinone in the body. These can include certain medications, sun exposure, and age. Statins, some beta-blockers, and certain blood pressure-lowering medications can all potentially reduce serum levels of CoQ10, while exposure to the sun's UV rays can often reduce levels in the skin. The body's natural ubiquinone synthesis usually decreases gradually beginning at age 21.

The normal amount of ubiquinone found in the human body is generally around two grams. People should consume or produce approximately 0.5 grams per day since it has an average turnover rate of four days. Most of those who consume a Western diet take in less than 5 mg of CoQ10 per day. It may be necessary for the elderly, people with certain illnesses, those taking certain medications, and others who cannot synthesize enough ubiquinone to take CoQ10 supplements if they are to reach the recommended 0.5 grams per day.

Ubiquinone plays important roles not only in the production of ATP, but also in maintaining the fluidity of cellular membranes and preventing oxidative damage by fighting free radicals. If free radicals cause oxidative damage to the DNA of cell mitochondria, the cell may no longer be able to function properly. This can potentially result in organ damage, including irreversible damage to the brain and heart.

CoQ10 supplementation has been used to treat a variety of conditions, including stroke, heart disease, gum disease, migraines, Parkinson's disease, mitochondrial disorders, and cancer. Its efficacy in treating many of these conditions is not yet clear, however. There is good evidence showing that CoQ10 supplementation can be helpful in treating those with mitochondrial or metabolic disorders which result in CoQ10 deficiency, as well as in modestly lowering high blood pressure. Although some evidence suggests that supplementation may also be helpful for other conditions, more well-designed studies need to be done to prove these claims.

Those who are considering taking ubiquinone supplements should generally alert their health care provider if they have allergies, especially to plants; are pregnant or nursing; are taking any medications or other supplements; or suffer from a blood platelet disorder or diabetes. Some people can experience allergic reactions to CoQ10 and should typically seek medical attention if they develop hives, experience difficulty breathing, or have swelling of the lips, tongue, face, or throat. CoQ10 can potentially interact with other medications or supplements, including diabetes and blood-thinning medications. It is not known whether CoQ10 can cause harm to unborn or nursing babies, and should generally be avoided by women who are pregnant or nursing.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:
















Discuss this Article
Post your comments